Goal - types , goal setting method and process
Goal
Goal is the target that we want to achieve. They act as the standard or criteria against which the results will be measured. Plans are documents which provide the outline about how the goals would be achieved. Simply, goal is the set target and plans include resource allocations, schedules, and other necessary actions to accomplish the goal.
Organisations never has a single goal for example earning profit cannot be the sole goal of the organisation. There are always multiple goals that an organisation pursue in order to achieve the comprehensive mission and vision statements of the organisation. These goals are of different types- different time periods, qualitative and quantitative, financial or people related etc. .
Strategic vs financial goals
A Financial goal is one which is related to the monetary aspect or the financial performance of an organisation. These are stated in numerical terms.
Example :- company A’s goal is to increase its net profit buy 6 to 8 % in next quarter.
Strategic goal involves statements of what you wish to achieve over the period of the strategic plan (e.g. over the next year, five years, ten years.) They reflect the analysis done while creating a vision, a role statement and a mission statement, and then analysis of environment, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Strategic goals must be connected to the strategic planning.
Example : strategic goal from Bloomberg L.P.: “We want to be the world’s most influential news organization.”7
Stated vs real goals
Stated goals are the official statements of what an organization says, and what it wants its stakeholders to believe, its goals are. Such statements are vague , qualitative and probably better represent management’s public relations skills than being meaningful guides to what the organization is actually trying to accomplish.
Example : Nike’s goal is “delivering inspiration and innovation to every athlete.”
Real goals are what the organisation is actually doing, what its real actions are. An organisation can say in its stated goals that we want to “succeed to serve” the society better but in real it may be working for making profits but not serving back. This example can be found in many NGOs running these days.
Other classifications
In addition to earlier discussed types these are somewhat similar and simpler classifications
- Qualitative goal:- minimum standard of service
- Quantitative goal:- minimum orders served per day
- Long term goal:- may take 2 years or more to achieve
- Short term goal:- typically 6 months to 1 year
- Organisational goal:- for the whole organisation
- Group goal:- for a team formed for a particular project
- Individual goal:- for one single employee
Setting Goals
Traditional Goal setting
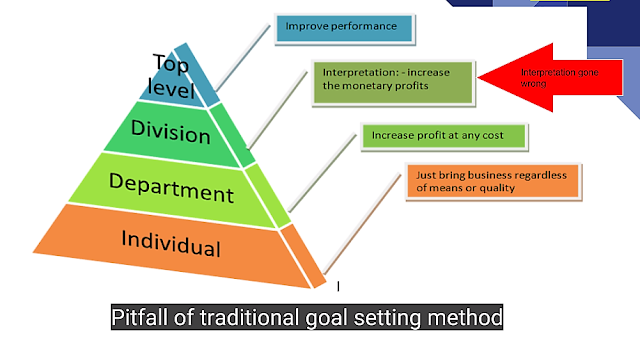
- Under traditional goal setting method, top management sets the goals to be achieved and then these goals are sent to lower departments where they are converted into departmental and then individual goals which are to be achieved by the employees.
- This method is based on the assumption that the top management can set more befitting goals as they have a better vision and clearer view of the bigger picture keeping in consideration the overall business environment.
- As the goals flow down to lower levels , managers apply their own interpretations to objective statements which can lead to misjudgment and thus non achievement of goals.
- As the goals are decided without much input from lower levels , the goals can be unrealistic and can lead to frustration among the lower level employees as a result of non achievement and too much pressure of work.
- Traditional method is successful in case of a small organisation where the owner itself is involved in day to day activities or It is successful where the line of authority or the structure of the organisation is very well defined and integrated with effective communication tools which do not let any misinterpretation take place and where feedback is considered important enough to reconsider the set goals.
Modern method of goal setting
- Management is an ever evolving discipline and there are new and improved ways of doing things being developed every day. One of such methods is Management By Objective or management by result is the process of setting goals which are mutually agreed upon by the manager and the employee and using the same to evaluate the performance later on.
- This method is based on the belief that employees are much more committed to the goals that they set by themselves or of which they have proper knowledge about before they are set for them.
- It is a bottom up approach where first the managers discuss the goals to be set for the next term with the concerned employees. This includes setting their targets and deciding on what terms will their performance be measured.
- Then these set goals are sent to the upper level for their approval .The top level if satisfied with the goals set , approves them or recommend any changes it feels are necessary. The recommendations are taken into consideration and relevant changes with the knowledge of employee are made .
- In order for MBO to work , it needs full top management backup. Also it includes lots of paperwork and meetings which should be appropriately assisted.
Setting Goals - steps
Review organisation’s mission
Mission is a broad statement about the organisations purpose and managers should review the mission statement before deciding up on goals to make sure that goals decided are in line with the mission statement of the organisation .
Example
In TED Talks, people participate to give short powerful talks about almost any topic in the world in order to educate, inspire and create rational thinking among people which correlates its mission statement of “spreading ideas”.
Evaluate available resources
The goals that one sets should be challenging but should also be realistic and achievable in terms of the resources which are available at the organisation. if we end up setting goals which require resources in terms of men, money or machines over and above what we have and what we can provide, we won't be able to achieve those goals no matter how hard everyone works.
Example
Say A’s sole source of income give him 20,000 rupees every month and after expenses he is able to save 2000 per month.
In this case , A can set a target of saving 24000 by the end of the year or maybe up-to 30,000 (by saving some money otherwise spent on leisure) but anything which is too beyond this say 80,000 or 100000 or more would be a WRONG GOAL set up by A .
Determine the goals individually or with input from others
Keeping the first two steps in mind, here we should determine or set the goals for the organisation. the goals should be realistic, achievable, futuristic, Include a time frame for their achievement and in similar lines with the organisational mission.
These goals can be set individually or with input from others depending upon the form of organisation and how work is done in it. As in case of small business where owner is involved in day to day activities, he/she sets the goals individually without much input from others.
In large scale organisations, there are teams formed of managers of different divisions who look after this work.
Write down the goals and communicate them to all who need to know
It is an important steps to share set goals in a written format with all the people who need to know them as it serves as an formal document and an evidence of the goals which have been set. It makes sure that people look at them and think about them thoroughly as it is not a verbal communication which can just go away. They are written and include standards against which the performance will be measured.
Review results and whether goals are being met
As the set goals are implemented the managers should check the results to find out if there are any deviations from the desired results. Whether deviations are positive or negative and how big .in case it is found that the goals set are incorrect they should be corrected immediately



Comments
Post a Comment